
A single bout of sleep apnea impacts the human body’s ability to regulate blood pressure, say researchers.

A single bout of sleep apnea impacts the human body’s ability to regulate blood pressure, say researchers.

Sleep disorders may precede and influence the disease course in neurological diseases, involving daytime functioning, quality of life, morbidity, and mortality.

Sleep apnea is an important disease of public health significance that increases mortality, stroke and cancer risk in a community based population.

This study was designed to determine whether reductions in morning systolic blood pressure (BP) elicited by treatment of moderate to severe obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) in heart failure (HF) patients are associated with a reduction in sympathetic vasoconstrictor tone.

The objectives of this article are to understand characteristics of the normal sleep cycle, including sleep stages, and changes with aging. Also for sleep disorders, categorize as hypersomnia, insomnia, parasomnia; for each disorder describe major clinical and physiological characteristics, and mechanisms if known.

Recent research in animal models and human population cohorts has shown that sleep apnea and, specially, intermittent hypoxia may worsen the prognosis of cancer.
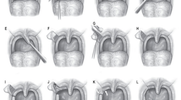
JCSM Journal of Clinical Sleep Medicine focuses on clinical sleep medicine. Its emphasis is publication of papers with direct applicability and/or relevance to the clinical practice of sleep medicine.
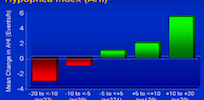
Gastric bypass surgery not only induces significant weight loss in successful patients but also leads to marked improvements in associated co-morbidities. A recent survey demonstrated that obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) occurs in up to 60% of patients undergoing bariatric surgery.

Objective To evaluate the effect of CPAP treatment on the incidence of hypertension or cardiovascular events in a cohort of nonsleepy patients with OSA.

Complete overview of OSA. Including sleep physiology, evaluation, prevalence, pathophysiology, medical treatment and surgical treatment.